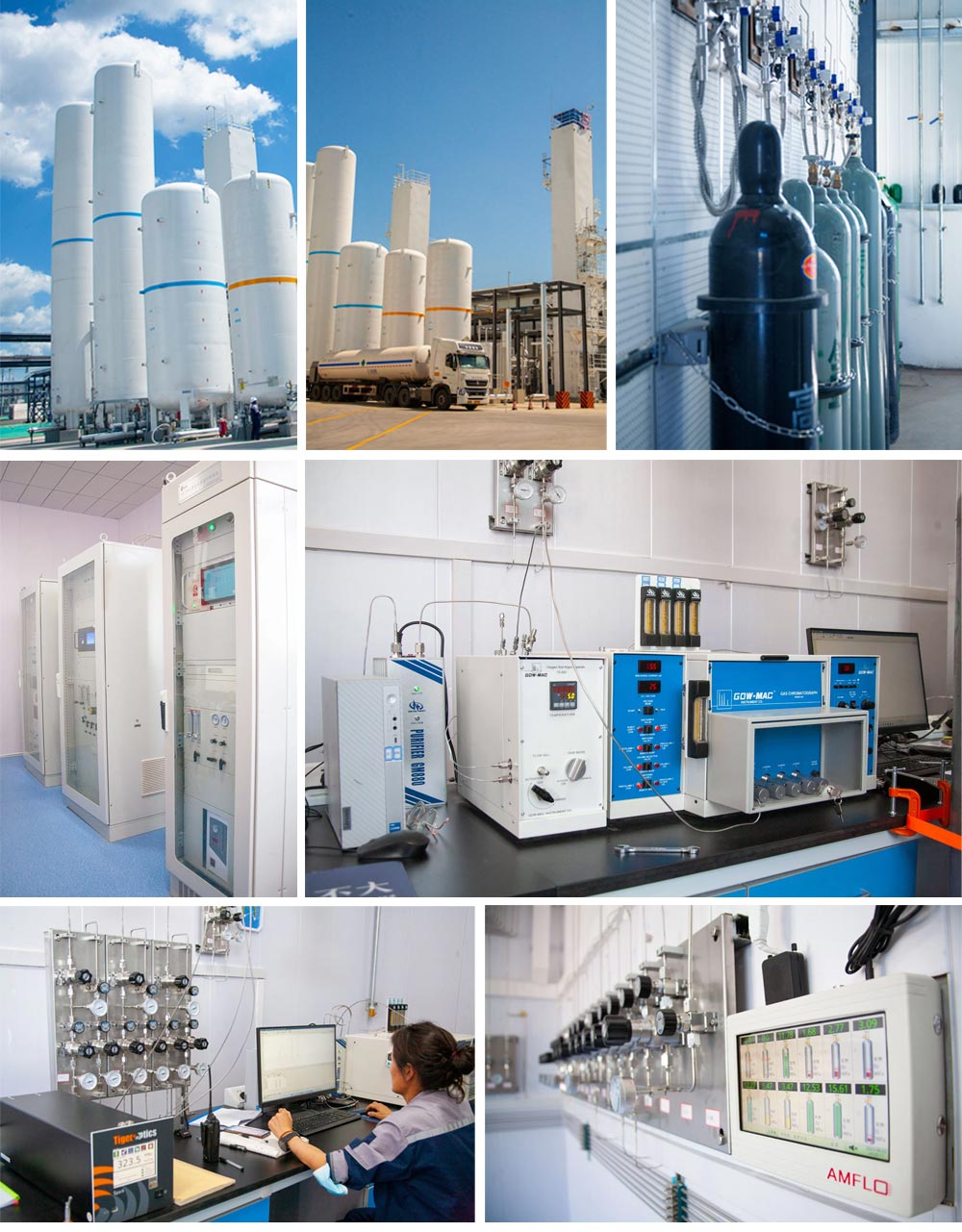
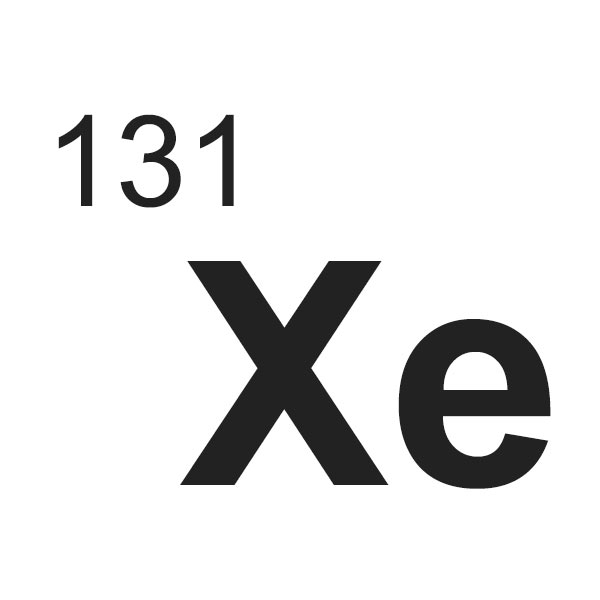Description
Product number: WT-LHY-XE131020
Natural abundance: 21.23%
Product abundance: 99.90%
Product specifications: 1L, 10L, 100L
Main application: Key materials for next-generation navigation nuclear magnetic resonance gyroscopes (NMRGs)
Xenon-131 (Xe-131) is a radioactive isotope of xenon, an element with atomic number 54 and symbol Xe. It is one of 35 known isotopes of xenon, and it is one of the most common isotopes of xenon, making up about 21.2% of the total abundance of xenon in the Earth’s crust.
Xenon-131 is a beta-decay radioisotope, which means that it decays by emitting a beta particle (an electron or positron) and an antineutrino. This process changes the atomic number of the atom by one, but it does not change the atomic mass. In the case of xenon-131, beta decay results in the formation of iodine-131 (I-131).
Xenon-131 has a half-life of 11.8 days, which means that it takes about 11.8 days for half of the atoms of xenon-131 to decay. This makes it a relatively short-lived radioisotope, and it is not used in many applications.
However, xenon-131 is sometimes used in medical imaging, particularly in thyroid scans. Iodine-131, the decay product of xenon-131, is concentrated in the thyroid gland, and it can be used to create images of the thyroid gland to detect abnormalities such as nodules or tumors.
Xenon-131 is also sometimes used in cancer treatment, particularly in the treatment of thyroid cancer. Iodine-131 can be used to destroy thyroid cells, which can help to shrink or eliminate tumors.
Here are some of the properties of xenon-131:
Atomic number: 54
Symbol: Xe
Mass number: 131
Half-life: 11.8 days
Mode of decay: Beta decay
Decay products: Iodine-131 (I-131)
Radiation: Beta particles (electrons or positrons) and antineutrinos